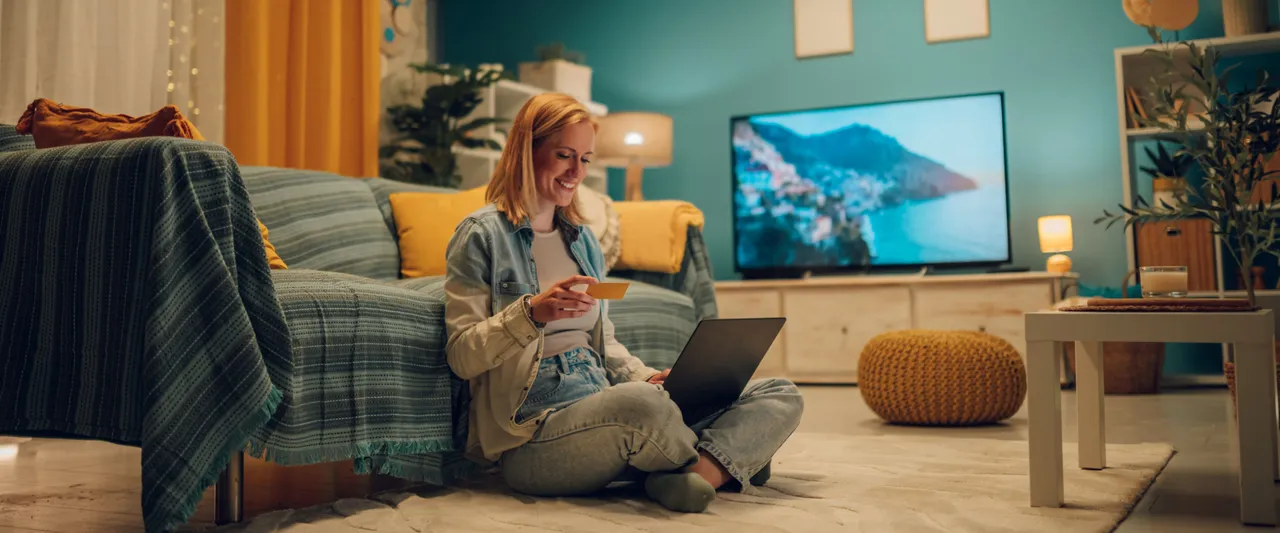
Ecommerce UX: an ultimate guide & noteworthy real-life examples
A great ecommerce website does more than showcase products—it guides customers through every stage of their journey, helping them make confident decisions by meeting their expectations and eliminating friction. That’s where ecommerce UX becomes critical: from intuitive navigation to clear content and seamless interactions, the user experience directly shapes how easily shoppers can discover, evaluate, and purchase what they need.
This is why ensuring a great user experience (UX) has become a top priority during ecommerce development. If you’re looking to optimize your ecommerce user experience, read on to find out how to do this right to improve your ecommerce store’s metrics.
Ecommerce UX defined
Ecommerce user experience, or UX, refers to how people interact with an online store and encompasses their ability to browse product categories, locate product descriptions and other key information, and complete transactions. The goal of ecommerce UX is to help website visitors achieve their goals with as little friction as possible.
While user experience and user interface are closely linked, they serve different purposes. UI includes the visual layout and all on-screen elements users see and interact with, such as buttons, menus, images, icons, and text. UX, on the other hand, focuses on the overall structure of the site and how users navigate it, including user flows, content organization, and how well the site supports task completion. So while a well-designed user interface contributes to a store’s visual appeal, it can’t compensate for usability issues, so when visitors struggle to find the right product, feel uncertain about the next steps, or face obstacles at checkout, they drop out. That’s why UX deserves just as much or even more attention as UI during an ecommerce development project.
Optimize your ecommerce site to improve its usability
How to improve key elements of ecommerce UX design
By refining the structure, behavior, and usability of individual pages and features, teams can make the ecommerce website more user-friendly and make tangible improvements to customer experience.
Homepage
The homepage is the ecommerce site’s main page, but it is rarely the customers’ first point of contact with the website, as they’re typically directed to product or category pages from ads or email links. Still, its design plays a key role in setting expectations, encouraging further exploration, and establishing trust.
- Showcase a broad range of product types to show variety and relevance
- Avoid auto-rotating banners on mobile devices, where they can become distracting and difficult to interact with due to limited screen space and slower internet
- Simplify language and currency selection with geotargeting and easy manual adjustments
- Remove visual or textual elements that can divert visitors from proceeding to other pages
The screenshots below are taken from the Vans ecommerce website. The online store has a well-structured homepage that highlights core product lines, new arrivals, and seasonal collections in a clear, scannable layout and helps visitors quickly identify relevant categories and continue exploring.

Vans homepage
Navigation
The website’s navigation should help users effectively find products or information. Its layout and product categorization should feel intuitive, helping reduce friction and keep visitors moving through an online store.
- Limit subcategories to ~10 items per level to prevent overwhelming users
- Don’t create shallow parent categories that contain only one or two items
- Surface high-demand content like “Bestsellers” or “Gift ideas” in relevant categories
- Use sticky navigation only if it doesn’t obstruct key page content
- Keep menus consistent across desktop and mobile screens, but adapt layouts, e.g., implement mega menus on desktop and accordions on mobile
- Add breadcrumbs to help users retrace their steps and highlight the shopper’s current location in the navigation flow, e.g., by making the active category bold
The screenshot below shows Amazon’s desktop navigation. Key sections, such as “Digital Content & Devices” and “Shop by Department”, are grouped logically, and frequently accessed areas, like “Best Sellers”, are placed near the top of the menu. After clicking on a certain category, a list of subcategories is loaded in a new panel. This structure avoids overwhelming the user, but the lack of collapsibility can slow down their exploration by requiring repeated back-and-forth actions.

Amazon navigation menu
On-site search
The search functionality in ecommerce websites is aimed at online shoppers who know what they’re looking for. Unlike navigation, on-site search serves as a shortcut, helping users reach their desired items faster.
- Ensure the search bar stands out with contrasting colors, bold borders, or an easily recognizable icon
- Prioritize a persistent search bar for a quick search
- Place exact matches at the top of the results page when queries match product names or SKUs
- Support natural language queries, including slang, abbreviations, and symptoms, e.g., “insomnia” for sleep aids
- Enable the autocomplete function with contextual suggestions, like categories or trending queries, as users type
- Include filters and sorting functionality in search results
- Highlight applied filters and allow their easy removal
- Provide spelling suggestions or automatic corrections in case of typos
- Avoid zero-result dead ends by suggesting alternatives or popular products
The Ray-Ban desktop website features a prominent on-site search functionality, accessible via a familiar magnifying glass pictogram in the header. Upon clicking this icon, a full-screen pop-up overlay appears, which eliminates distractions and directs users’ attention to the search interface. The pop-up layout is structured into three clear sections:
- “Popular Searches”, clickable suggestions that automatically populate the search bar
- “Popular Items”, product images with their names and prices linking directly to item pages
- “Useful Links”, including “Get Support”, “FAQ”, “Instore & Online Services”, and “The Ray-Ban Protection Plan”
As users begin typing, they can see text-based autocomplete suggestions and product images that are relevant to the request. The pop-up also allows for product filtering, shows the result count, and provides sorting options, offering more control over the search results.

Ray-Ban on-site search
Product listing
Product listing pages present the results of browsing or searching and often help users compare multiple items. A well-designed listing page makes it easier for shoppers to scan product options, apply filters, and make informed decisions without needing to visit each product page.
- Display the total item count clearly at the top and bottom of the list for users to understand the quantity of relevant items
- Replace pagination and infinite scroll with a “Load more” button
- Support essential sorting options, such as price, rating, and popularity
- Show average ratings and review counts for each product
- Implement checkboxes for filters to simplify the selection
- Use distinct formatting, such as fonts and spacing, to highlight prices, titles, and other key details
- Include a dedicated Sale/Deals filter to help users quickly identify discounted items
- Provide multiple thumbnail views (3+ images per product) to minimize unnecessary clicks
- Display applied filters with removal options
Below you can see the Pandora website’s product listing page. There, items are presented with images and prices, eliminating the need to open a product page. Each product image changes upon hover, revealing an alternate view, and a heart icon allows for quick product addition to a wish list. A string of sorting options enables shoppers to narrow broad categories. Moreover, the filtering pop-up offers filters such as “Metal”, “Price”, “On Sale”, “Collection”, “Color”, and “Theme”, along with product counts and checkboxes.

Pandora product listing page
Product page
Product pages are where most purchase decisions are made, with nearly all conversions involving at least one product page visit. Here, shoppers expect clear product images, detailed product information, and prominent calls to action to get a full view of the items and make a purchase decision.
- Include 3-5 high-quality images showing key product features in favourable angles
- Add product videos for items that are complex or require demonstration
- Implement collapsible sections for specifications or FAQs to reduce clutter
- Make the “Add to Cart” button prominent and persistently visible and place it above the fold
- Display pricing clearly with all applicable charges and discounts
- Show inventory availability per variant (size or color) in real-time
- Allow customers to access return and delivery policies right from the product page without page exits
- Incorporate user-generated content, such as reviews and photos, for social proof
- Allow for easy comparison with similar or complementary products
- Enable image zoom functionality for detailed inspection
- Consider implementing AR previews or 360° views for products where spatial context matters
The Michael Kors product page effectively presents an item with multiple high-quality images from various angles. The “Add to Cart” button is prominently displayed above the fold, alongside transparent pricing. The page also features similar items, facilitating comparison with other products, and a “You May Also Like” section, increasing the average order value.

Michael Kors product page
Shopping cart
The shopping cart is where potential customers finalize their purchase decisions. To avoid cart abandonment, the shopping cart page design should be developed in a way that lets users easily view their items, adjust the order, and confirm all costs before proceeding to payment.
- Show an accurate summary of products with quantities, thumbnails, and prices
- Enable quantity adjustments and item removal without leaving the page
- Display all costs upfront, including subtotals, taxes, and shipping rates
- Keep the checkout button visually prominent and persistently available
- Provide estimated shipping timeframes and access to a return policy
- Show inventory alerts for low-stock items
- Let users save their cart or email it to themselves
- Include progress indicators for free shipping thresholds
The IKEA shopping cart page provides a clear overview of the selected item with options for delivery or in-store pickup, including associated costs and availability. The product has a clear image, name, price, and quantity selector.

IKEA shopping cart page
A concise “Order summary” panel on the right details product prices and the total cost before tax, allows for applying a discount code, and features a prominent call to action for proceeding to the checkout. Under the button, a potential customer can see the accepted payment method. Below the main cart, there is an “Easy picks” section that displays suggested complementary products with their images, prices, and availability, encouraging shoppers to add more goods to their cart without leaving the page.
Checkout & order confirmation
The checkout is the final step in the customer journey, where shoppers provide their shipping, billing, and payment details to complete the purchase. Here, it’s essential to streamline form completion and ensure clear order verification and confirmation.
- Offer guest checkout alongside account creation and login
- Use single-page checkout or a clearly segmented multi-step checkout format layout
- Auto-fill address and payment details when possible
- Provide visual confirmation after each key action, such as address validation, payment processing, or promo code application
- Show a final order summary before submission
- Display multiple payment options, such as credit cards, PayPal, Apple/Google Pay, installment payment, and platform-specific methods like Shop Pay for Shopify
- Confirm the order with a dedicated pop-up or page with a clear success message and essential order details, such as the order number, payment status, delivery address, selected shipping method, estimated delivery date, and a summary of purchased items with images and pricing
The Victoria’s Secret checkout page uses a segmented, multi-step layout with “Shipping”, “Payment”, and “Review” tabs at the top. The “Shipping” section prominently displays the required fields for address and contact information so that all necessary details could be captured. Multiple shipping methods are available, each with an estimated delivery date and corresponding cost. A persistent “Order Summary” on the right displays subtotal, shipping, and total costs, providing transparent pricing and the ability to return to the shopping cart.

Victoria’s Secret checkout page
Get expert insights into how to improve your online store
Additional ecommerce UX best practices
Beyond optimizing individual website elements, retail companies can also apply practices that elevate the overall online shopping experience across the website, strengthen customer satisfaction, and improve the online store’s metrics. These practices help ecommerce businesses create websites that align with user expectations and remove friction across all touchpoints, leading to increased sales and higher revenue.
Optimize UX for mobile devices
Mobile devices generate nearly 80% of global retail website traffic. However, they are still behind desktops in terms of conversion rates, meaning that customers prefer bigger screens and the perceived security of personal computers when making purchases. For ecommerce businesses, this gap highlights the need to improve mobile ecommerce UX to win over mobile shoppers.
- Follow responsive web design principles, adjusting layout, images, and content based on device screen size and orientation
- Size and space out elements like buttons, filters, or image carousels so that users can conveniently tap them with the fingers of one hand
- Place mobile navigation at the bottom of the screen for easier thumb access
- Include a “View All” option in the navigation menu to let users access broader product lists
- Use full-screen search overlays to improve the visibility of the search interface
- Enable advanced search options like barcode, voice, or image search
- Place essential content and primary CTAs above the fold but avoid crowding them
- Apply mobile-specific design elements like sticky menus, collapsible sections, and checkout forms with autofill capabilities
- Test the website’s mobile version in live environments on different devices, operating systems, and network speeds to verify its usability
Mobile-friendly experiences increase the chances that users will complete their purchases on their phones rather than switching to a desktop. They also help preserve customers’ purchase intent, reducing the risk of distraction or drop-off. Ecommerce sites that prioritize mobile usability can benefit from higher conversion rates, stronger engagement from mobile-first shoppers, and a competitive advantage.
Enhance site performance
Slow website speed can undermine user experience and be a reason for lower search engine rankings. According to an analysis of over a million domains, top-ranking pages load in around 1.65 seconds. This means that retailers should aim for a loading speed of 2 seconds or less when performing website performance optimization, especially on mobile devices where network conditions are less reliable.
- Audit site performance with tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, or Pingdom and regularly monitor it, especially after adding third-party extensions or themes
- Compress product images, use modern file formats like WebP, and employ lazy image loading
- Eliminate excessive animations
- Defer unnecessary JavaScript code and avoid plugins that block rendering
- Use server-side caching and deploy a content delivery network (CDN) to reduce server load and deliver content faster to users based on their geographic location
Website load time is a critical aspect of ecommerce UX, directly influencing how effectively shoppers move through a user journey and whether they complete their purchase. Ecommerce websites that allow for fast, uninterrupted browsing across devices create better first impressions, have lower bounce rates, and maintain greater search visibility.
Collect data to understand user behavior & preferences
To design for real user needs, ecommerce businesses need to analyze various types of data, such as behavioral, attitudinal, and transactional, to understand how visitors interact with the site and where friction occurs. These insights help validate assumptions and guide decisions around navigation, content structure, and feature design.
- Track full user journeys using session replay tools and funnel analytics
- Employ heatmaps to analyze which parts of a page users engage with most and which they tend to overlook
- Configure on-page surveys and post-purchase feedback forms to capture user sentiment
- Run five-second tests to validate your value proposition and messaging clarity
- Study high-exit pages and mitigate the discovered issues
- Conduct usability testing, with real users explaining their decisions and highlighting confusion points
A data-driven approach ensures that UX improvements are grounded in actual user behavior, so it’s important for ecommerce companies to consistently gather insights from multiple sources to refine their website design, reduce friction, and better align with customer expectations.
Structure UX around purchase journeys
Shoppers don’t always start their journey on a homepage or follow a linear path to purchase, but instead land where the brand’s campaigns, search engines, or social media links send them. For this reason, it’s essential to treat every page, whether it’s a product or category one, as a potential entry point and structure their UX to facilitate immediate understanding of the context.
- Make sure each entry point includes key product details, pricing, and CTAs, so visitors can make decisions without needing to visit other pages
- Align landing page content with the messaging used in ads or external links
- Avoid navigation dead ends by adding links to related products, support options, or value statements
- Place links to customer support, shipping policies, and guarantees near key decision points, such as “Add to Cart” or checkout buttons
A website structure optimized for simplifying purchases across all pages reduces bounce rates, improves user flow, and increases conversion opportunities. Every touchpoint should help visitors take the next step without forcing them to backtrack or search for missing information.
Final thoughts
Great ecommerce UX goes beyond visual appeal, contributing to higher customer satisfaction, improved sales, and better SEO performance. Regardless of the device used, the experience should feel effortless to your customers. When designed with usability in mind, an ecommerce website helps you convert more users, secure return visits, and build long-term loyalty.
If you’re looking to improve your store’s user experience, Iflexion can help you at every stage of your journey. We design and develop user-friendly ecommerce websites and mobile apps, deliver actionable redesign plans, and improve your ecommerce UX to support your business goals.
Work with ecommerce experts to turn your store’s UX into a competitive advantage